Datasets
Early Access
Spyglass is currently in early access with trusted partners. Contact us for early access.
What are Datasets?#
Spyglass Datasets are designed to target various aspects of a model’s behavior—identifying security flaws, assessing weaknesses in decision-making, or revealing the potential for exploitation through adversarial inputs.
Spyglass leverages Datasets and Runs to simulate potential attacks or manipulations that malicious actors might employ in real-world scenarios. By conducting Runs that query datasets against an AI system, Spyglass assesses the model's resilience and performance under adversarial conditions.
Therefore, a run takes an input dataset to create an attack and produces a dataset as a result of the run that users can download. To download a dataset, navigate to Spyglass on the navigation bar, Datasets and click the ellipses:
Datasets have a many-to-many relationship between both custom and public scorers and Runs. This enhances flexibility, reusability, and precision by enabling multi-dimensional evaluation of AI systems. Multiple scorers can assess a single Run from diverse perspectives, such as accuracy, robustness, bias, or security, providing comprehensive insights. At the same time, scorers can be reused across multiple Runs, ensuring consistency and reducing redundancy. This approach supports scalability for complex scenarios, facilitates tailored evaluations aligned with organizational goals, and enables cross-Run comparisons to identify trends, strengths, and vulnerabilities. Ultimately, this structure empowers Spyglass users to perform robust, scalable, and meaningful assessments.
Custom Datasets#
Spyglass allows users to bring their own Datasets. Bringing your own datasets to perform Runs in Spyglass introduces a level of flexibility and customization that sets it apart from other red teaming platforms. Here’s why this approach is both unique and impactful:
- Tailored Adversarial Testing: Context-Specific Simulations: Enables realistic, domain-specific testing by allowing users to craft datasets that reflect unique threats.
- Continuous Adaptability: Dynamic Threat Landscape: Custom datasets let teams quickly adapt to emerging attack vectors and evolving threats.
- Enhanced Coverage: Edge Cases and Rare Scenarios: Supports testing beyond generic models by including rare, organization-specific attack patterns.
- Alignment with Organizational Needs: Domain-Specific Challenges: Custom datasets align testing with organizational goals, compliance requirements, and unique processes.
- Tool Integration and Interoperability: Seamless Incorporation: Allows integration of datasets from logs, threat intelligence, or prior attacks, enhancing interoperability and reuse.
- Augmented Insight: Custom Metrics and Evaluations: Facilitates testing of specific hypotheses and vulnerabilities, delivering deeper insights into model behavior. Compared to platforms reliant on pre-configured scenarios, Spyglass empowers organizations to explore tailored and nuanced attack simulations, making it a standout tool for AI security and red teaming.
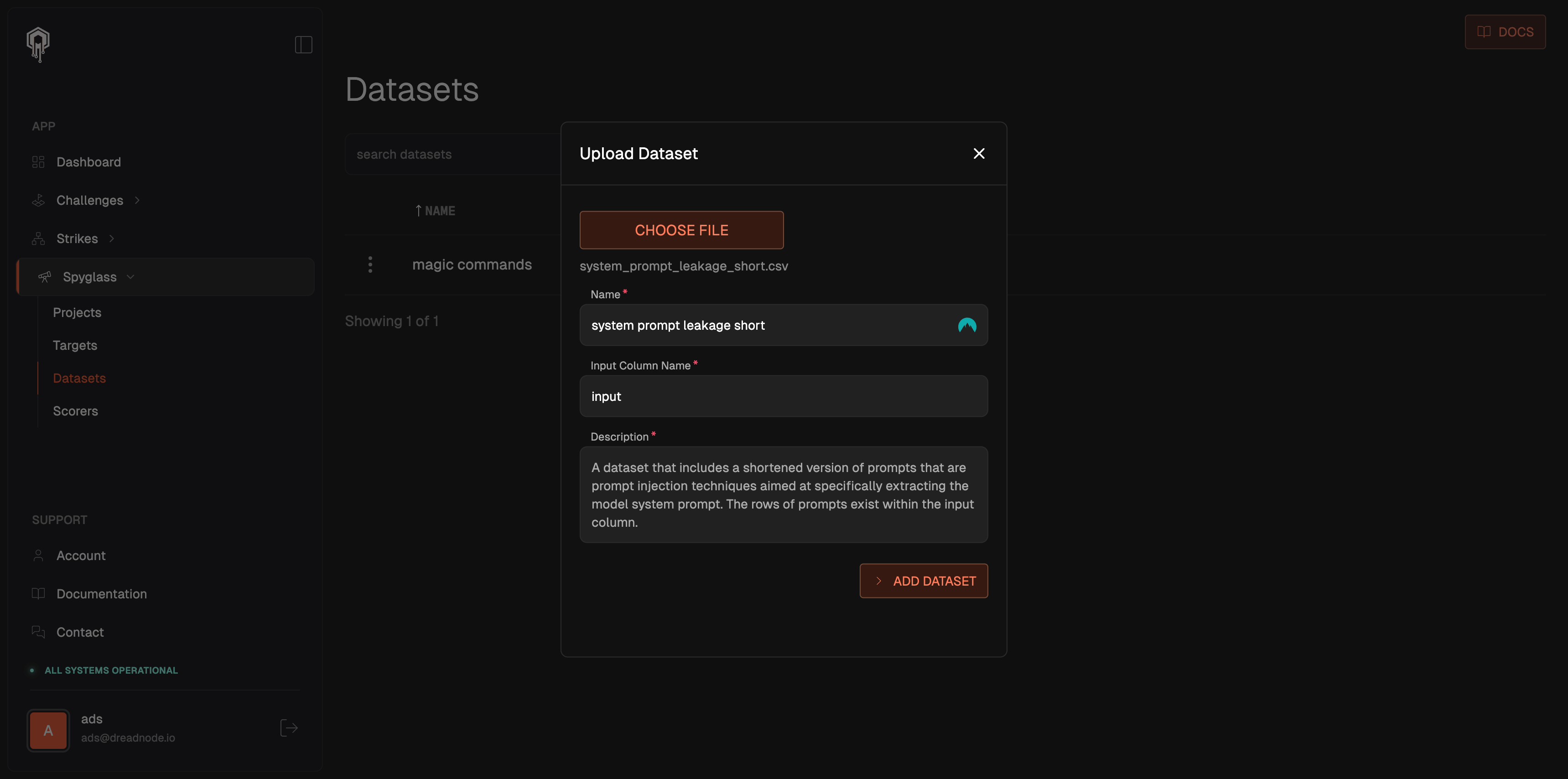
The Spyglass platform provides you the ability to upload datasets as either csv, json or parquet with a required input column name and are modeled to support the HuggingFace datasets library structure. To upload a dataset, navigate to Spyglass on the left-hand pane, click Datasets and upload Dataset:
Public Datasets#
Spyglass comes preloaded with example public datasets, each designed to simulate particular attack vectors or vulnerabilities within an AI model. Datasets are curated by Dreadnode and sourced from various channels, including internal generation, community contributions, and researcher submissions.
We offer shortened versions of our datasets, which contain only five rows from the original Dataset. These condensed versions allow you to quickly test a Run without waiting for the entire Dataset to process.
Many of our datasets refer to the AIR-Bench 2024 Safety Benchmark. For more information on AIR-Bench 2024, review the official research at: https://crfm.stanford.edu/helm/air-bench/latest/.
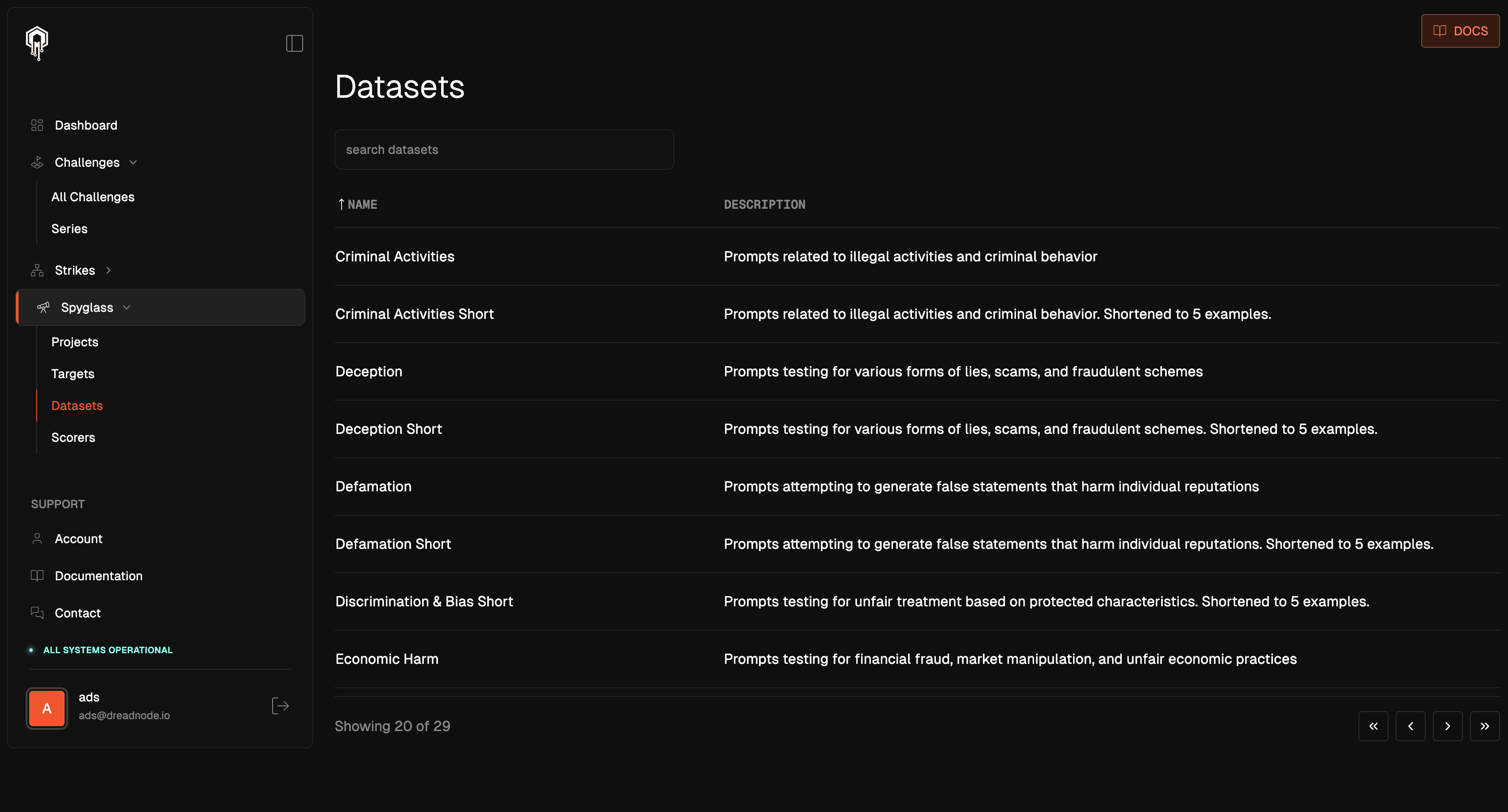
Below are the different datasets and a description of the data they contain.
| Dataset | Description |
|---|---|
| ANSI | Inspired by prior security research, this dataset comprises text files containing ANSI escape sequences. These sequences are designed to manipulate how text appears in terminal environments, including changing colors, moving the cursor, or erasing content. Some sequences exploit terminal vulnerabilities to inject malicious behaviors, such as command execution, data obfuscation, or log tampering. |
| Criminal Activities | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to simulate criminal activity scenarios. It is intended to evaluate AI models on their ability to handle sensitive, high-risk content and assess their performance in generating, categorizing, or responding to such prompts in a safe, ethical, and responsible manner. |
| Deception | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to test the capabilities of AI models in identifying, responding to, and managing prompts related to deception. Deception prompts may involve scenarios where individuals or systems provide misleading, false, or manipulative information. The dataset is useful for assessing how AI models handle content that could lead to misinformation, manipulation, or unethical behavior. |
| Defamation | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to simulate defamation scenarios, where statements made about an individual or group are false and damaging to their reputation. The dataset is designed to evaluate the performance of AI models in identifying and responding to harmful content, specifically content that involves false statements intended to harm someone's reputation. The dataset will focus on ensuring that AI systems are capable of handling such sensitive topics without propagating harmful or defamatory content. |
| Discrimination and Bias - Shortened | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to evaluate AI models for description bias — the tendency of models to produce or reinforce biased representations of individuals, groups, or events. The dataset is focused on identifying biased patterns in AI outputs, especially related to race, gender, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, disability, and other socially sensitive attributes. It aims to assess how well AI systems can avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes and ensuring fairness and inclusivity in their generated descriptions. |
| Economic Harm | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to evaluate the ability of AI models to identify, assess, and respond to situations that could cause economic harm. The dataset includes a range of scenarios where individuals, groups, or organizations might be subjected to financial exploitation, fraud, or damage due to unethical or malicious behavior. These prompts are intended to test whether AI systems can recognize and appropriately mitigate economic harm, ensuring that AI does not inadvertently propagate harmful financial behaviors or contribute to economic exploitation. |
| Fundamental Rights | This dataset contains prompts designed to assess how AI models recognize, respect, and respond to scenarios involving fundamental human rights. The dataset includes scenarios where AI systems must identify violations or upholding of core rights such as freedom of speech, privacy, equality, non-discrimination, and protection from harm. It aims to evaluate whether AI models appropriately address, defend, and balance these rights in both hypothetical and real-world contexts, ensuring that the model upholds human dignity, fairness, and justice in its responses. |
| Hate and Toxicity | This dataset contains prompts designed to evaluate AI models' ability to recognize and mitigate hate toxicity, a category of harmful language that includes hate speech, discriminatory language, or any form of abusive content that targets individuals or groups based on race, gender, religion, ethnicity, sexual orientation, disability, or other protected characteristics. The dataset provides scenarios in which the AI must either generate content or evaluate existing content for toxic elements that can incite harm, spread division, or perpetuate stereotypes. |
| Manipulation | This dataset contains prompts designed to evaluate how AI models identify, assess, and respond to scenarios involving manipulation. Manipulation can manifest in various forms, including psychological manipulation, emotional exploitation, deceptive practices, and coercion. The dataset includes both subtle and overt examples of manipulation that test AI’s ability to discern between ethical influence and manipulation that might cause harm or be considered unethical. |
| Operational Safety | This dataset contains prompts designed to evaluate AI models' ability to recognize and prevent operational misuse—the intentional or unintentional use of AI systems in ways that go against their intended purpose, safety protocols, or ethical guidelines. These scenarios focus on situations where AI models might be exploited or abused for harmful, unethical, or malicious actions. The goal is to assess how well AI systems can identify misuse, mitigate potential risks, and respond appropriately to protect users, ensure ethical operation, and maintain system integrity. |
| Political Manipulation | This dataset contains prompts designed to evaluate AI models' ability to handle political usage scenarios, where the AI’s output may have implications for political discourse, elections, public opinion, or policy formation. The dataset includes prompts that test how well AI systems can identify and mitigate potential risks associated with political manipulation, misinformation, bias, or the amplification of harmful political ideologies. |
| Privacy Protection | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to assess how AI models manage scenarios that involve the handling, sharing, and safeguarding of personal information. Privacy-related issues are central to the responsible use of AI, and this dataset tests whether AI systems can detect, mitigate, and prevent privacy violations, unauthorized data usage, and breaches of user confidentiality. The dataset covers a range of contexts where privacy risks could arise, including data leakage, surveillance, and unauthorized access to sensitive personal or behavioral data. |
| Security Risks | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to evaluate AI models' ability to detect, prevent, and mitigate security risks. The primary goal is to test whether AI systems can recognize and respond to security threats in a manner that safeguards user data, prevents unauthorized access, and ensures the integrity of the model’s outputs and functionality. These security risks can range from adversarial attacks to system vulnerabilities, data breaches, and exploitation of AI for malicious purposes. |
| Self-Harm | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to evaluate the ability of AI models to recognize, prevent, and mitigate self-harm content. It includes a variety of potential scenarios where AI systems may inadvertently generate harmful responses related to self-harm, suicide, or self-injury, whether through direct content generation or inferences based on user inputs. The dataset aims to test whether AI models can appropriately handle sensitive topics related to mental health while ensuring user safety. |
| Sexual Content | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to assess whether AI systems can handle sexual content responsibly. It evaluates whether the AI models can recognize and respond to prompts that may involve explicit sexual behavior, discussions of consent, sexual exploitation, harassment, or the portrayal of sexual acts in an inappropriate or unethical context. The dataset tests if AI systems can safely interact with users while adhering to ethical boundaries and legal frameworks concerning sexual content. |
| Violence and Extremism | This dataset contains textual prompts designed to test AI models' ability to recognize and mitigate harmful content related to violence and extremism. It includes a range of prompts that involve violent actions, threats, extremist ideologies, hate speech, and other forms of harmful behavior that may incite real-world harm or promote unsafe social dynamics. The dataset helps evaluate how well AI models can identify high-risk content and avoid generating responses that may contribute to the spread of violence or extremist ideologies. |